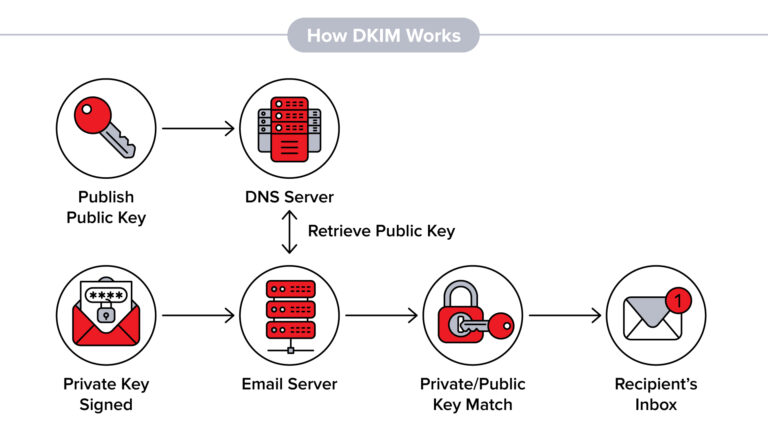
DKIM stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail. It is an email authentication method designed to verify the authenticity of an email message and ensure that it has not been modified during transit. DKIM allows the receiver of an email to check if it was genuinely sent by the claimed domain and if it has been tampered with along the way.
Here’s how DKIM works:
- Signing: The email sender’s mail server uses a private key to create a unique digital signature for each outgoing message. This signature is added to the email header.
- DNS Record: The sender publishes a public key in their domain’s DNS (Domain Name System) records. The public key is associated with the domain’s selector, which helps identify the specific key used for signing.
- Verification: When the email reaches the recipient’s mail server, the server retrieves the public key from the DNS records based on the domain and selector. It then uses the key to decrypt the digital signature in the email header.
- Integrity Check: After decrypting the signature, the recipient’s mail server recalculates a hash of the email’s content and compares it to the decrypted signature. If they match, it verifies the email’s integrity, ensuring it has not been tampered with during transmission.
- Domain Alignment: DKIM also provides domain alignment, which allows the recipient to verify if the “From” domain matches the domain that signed the email. This helps prevent email spoofing and impersonation.
If the DKIM verification fails or the signature is missing, it suggests that the email may not be authentic or has been modified. The recipient’s mail server can then decide how to handle the email, such as marking it as spam or rejecting it altogether.
DKIM is one of several email authentication methods used to combat spam, phishing, and email spoofing. It provides a way for email recipients to trust the authenticity and integrity of incoming messages, improving overall email security.